Introduction
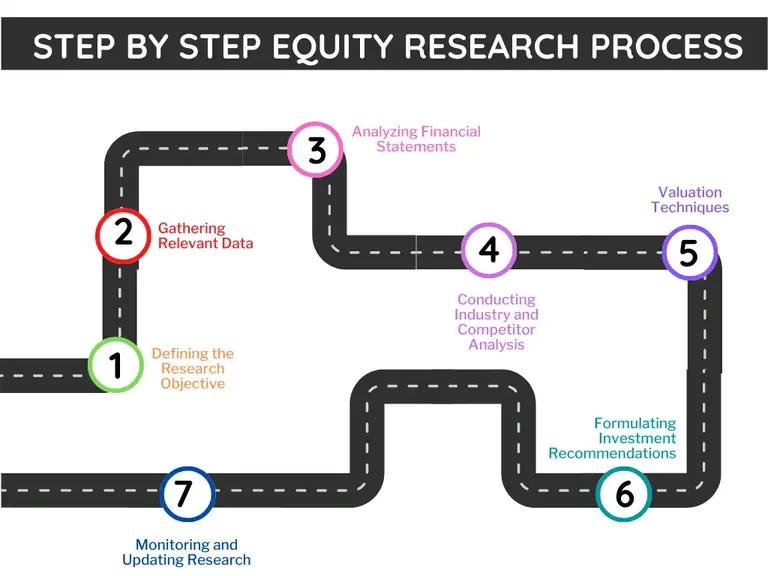
Equity research plays a crucial role in finance by providing valuable insights and analysis to investors and financial professionals. This article will explore the step-by-step procedure of equity research, covering everything from defining the research objective to formulating investment recommendations. By following these steps, analysts can generate comprehensive research reports that assist investors in making informed choices.
Understanding Equity Research Process
Before diving into the process, let’s understand what equity research is and why it is important. Equity research involves analyzing financial data, market trends, and industry dynamics to evaluate the performance and potential of publicly traded companies. It aims to provide investors with insights into the value and risks associated with specific stocks. Analysts can recommend buying, selling, or holding stocks by conducting thorough equity research, helping investors make informed decisions.
Step 1: Defining the Research Objective
Defining the equity research objective is a critical step in the equity research process. It lays the foundation for the entire analysis and helps ensure the research is focused and aligned with the intended purpose. This step involves identifying the purpose of the study and setting clear goals that guide the subsequent analysis.
The Importance of Defining the Equity Research Objective
Defining the equity research objective is crucial for several reasons:
- Focused Analysis: By clearly specifying the research objective, analysts can narrow down their scope of analysis. It helps them concentrate on specific aspects of the company or industry and avoid unnecessary distractions. It allows for a more focused and targeted approach to the research process.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: A well-defined research objective helps allocate resources effectively. It ensures that analysts invest their time and effort in collecting and analyzing relevant data, directly contributing to achieving the research goals. It prevents wasted resources on irrelevant or tangential information.
- Clarity in Communication: Defining the research objective enhances the clarity of communication between analysts and investors. It helps set the right expectations regarding the analysis and the outcomes. It ensures that the research is aligned with investor needs and provides valuable insights.
Factors to Consider in Defining the Research Objective
To define the equity research objective effectively, several factors need to be considered:
- Identifying the Purpose: Analysts must identify the purpose of the research. Is the research objective to evaluate the company’s financial performance, assess its growth prospects, or analyze the industry dynamics? Understanding the purpose helps shape the direction of the research and determines the focus of the analysis.
- Setting Clear Goals: Clear goals provide a roadmap for the research. Goals can include assessing the company’s competitive position, analyzing its profitability drivers, or evaluating the impact of industry trends. These objectives must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to ensure clarity and focus.
- Target Company or Industry: Defining whether the research objective concerns a specific company or industry is crucial. For example, the aim may be to analyze a company’s financial health or assess a particular industry’s growth potential. It helps narrow down the research scope and tailor the analysis accordingly.
Aligning the Research Objective with Investor Needs
Defining the equity research objective should also involve aligning it with investor needs. Understanding the target audience and their investment preferences, risk tolerance, and investment goals is important. This alignment ensures that the research addresses relevant investor concerns and provides insights that support their decision-making process.
By aligning the research objective with investor needs, analysts can deliver research reports tailored to their audience, providing them with valuable information to make informed investment decisions.
Defining the equity research objective is a critical step in the equity research process. It provides focus, clarity, and direction to the analysis that follows. Analysts can conduct research that delivers meaningful insights and supports informed investment decision-making by identifying the purpose, setting clear goals, considering the target company or industry, and aligning the research objective with investor needs.
Step 2: Gathering Relevant Data
Gathering relevant data is a crucial step in the equity research process. It involves collecting comprehensive and accurate information to support analyzing and evaluating a company’s performance, financial health, and market dynamics. This step lays the foundation for conducting in-depth research and making informed investment decisions.
The Significance of Gathering Relevant Data in Equity Research
Gathering relevant data is of utmost importance in equity research for several reasons:
- Informed Analysis: Relevant data provides analysts with the necessary information to thoroughly analyze a company. It allows them to understand the company’s financial position, industry trends, market dynamics, and competitive landscape. This analysis forms the basis for generating meaningful insights and making informed investment recommendations.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The quality of the data gathered directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the research findings. Analysts can make data-driven investment decisions by ensuring that relevant and reliable data is collected, reducing reliance on assumptions or guesswork.
- Risk Mitigation: Gathering relevant data helps identify potential risks associated with an investment. It enables analysts to assess the company’s financial stability, debt levels, and exposure to market volatility. This assessment helps investors understand the risks involved and make informed decisions to mitigate potential risks.
Sources of Data for Equity Research
To gather relevant data for equity research, analysts rely on various sources, including:
- Company Reports and Financial Statements: Company reports, such as annual reports, quarterly reports, and investor presentations, provide valuable information about a company’s operations, financial performance, and strategic initiatives. Financial statements, including the income/profit and loss statement, balance sheet, and cash flow report, offer insights into the company’s revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and cash flows.
- Market Data and Economic Indicators: Market data, such as stock prices, trading volumes, and market indices, provide information about the company’s stock performance and broader market trends. Economic pointers, such as GDP growth rates, inflation data, and interest rates, help assess the macroeconomic environment and its potential impact on the company.
- Industry Research and News Sources: Industry research reports, sector-specific publications, and news sources provide information about industry trends, competitive dynamics, regulatory changes, and market developments. These sources offer valuable insights into the industry’s outlook and the company’s positioning within the sector.
- Regulatory Filings and Disclosures: Regulatory filings, such as the company’s annual 10-K report, 10-Q quarterly reports, and proxy statements, contain detailed information regulatory bodies require. These filings provide insights into the company’s corporate governance practices, executive compensation, and potential legal or regulatory risks.
Data Collection and Analysis
Once the relevant data is identified, analysts need to collect and analyze it effectively. It involves the following steps:
- Data Validation and Quality Assurance: Analysts must validate the data to ensure its accuracy and reliability. They review the data for consistency, completeness, and integrity. Data quality assurance procedures, such as cross-referencing data from multiple sources, help identify and rectify discrepancies or errors.
- Organizing and Managing Data: Analysts organize and manage the collected data in a structured manner to facilitate analysis. It may involve creating spreadsheets or databases or using specialized data management tools. Proper organization of data enables efficient analysis and easy retrieval when needed.
Gathering relevant data is a crucial step in the equity research process. It provides analysts with the necessary information to perform in-depth analysis, make informed investment decisions, and mitigate risks. By utilizing reliable data sources and implementing effective data collection and analysis practices, analysts can ensure the accuracy and reliability of their research findings, contributing to successful equity research outcomes.
Step 3: Analyzing Financial Statements
Analyzing financial statements is a crucial step in the equity research process. It involves examining a company’s financial statements to gain insights into its financial performance, profitability, liquidity, solvency, and cash flow generation. This analysis helps equity researchers understand the company’s financial health and make informed investment decisions.
The Significance of Analyzing Financial Statements in Equity Research
Analyzing financial statements holds significant importance in equity research for the following reasons:
- Evaluation of Financial Performance: Financial statements provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance over a specific period. Analyzing these statements allows equity researchers to assess the company’s revenue generation, cost structure, profitability, and overall financial stability. This evaluation is crucial for understanding how effectively the company operates and generates returns for its shareholders.
- Assessment of Risk and Return: Financial statement analysis helps analysts evaluate the risks and potential returns associated with investing in a company. Analysts can gauge the company’s ability to withstand economic downturns, meet its financial obligations, and generate consistent returns for investors by examining its financial health, liquidity position, and debt levels.
- Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses: Analyzing financial statements helps identify a company’s strengths and weaknesses. By scrutinizing key financial metrics and ratios, analysts can identify areas where the company excels, such as strong revenue growth, high-profit margins, or efficient cost management. It also helps uncover potential weaknesses, such as declining profitability, excessive debt, or working capital issues.
Key Financial Statements for Analysis
The primary financial statements used for analysis in equity research are:
- Income Statement: Also identified as the profit and loss report, the income statement summarises a company’s income, expenses, and net income over a specific period. It highlights the company’s revenue sources, cost of goods sold, operating fees, and other expenses. Analysts use the income statement to assess the company’s revenue growth, profitability, and operating efficiency.
- Balance Sheet: The balance sheet delivers a picture of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It presents the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. Analysts analyze the balance sheet to evaluate the company’s liquidity, solvency, asset composition, and capital structure.
- Cash Flow Statement: The cash flow report tracks a firm’s cash inflows and outflows throughout a specific period. It categorizes cash flows into operating, investing, and financing activities. Analysts use the cash flow statement to assess the company’s cash flow generation, ability to meet its financial obligations, and investment or financing decisions.
Analytical Techniques for Financial Statement Analysis
Equity researchers employ various analytical techniques to analyze financial statements effectively. Some common methods include:
- Ratio Analysis: Ratio analysis involves calculating and interpreting financial ratios derived from financial statements. Ratios such as profitability, liquidity, and leverage ratios provide insights into the company’s financial performance, efficiency, and risk profile.
- Trend Analysis: Trend analysis involves comparing financial statement data over multiple periods to identify patterns and trends. It helps analysts assess the company’s historical performance and identify changes or developments.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparative analysis involves comparing a company’s financial performance with its peers or competitors. This analysis helps benchmark the company’s performance, identify areas of outperformance or underperformance, and gain insights into its competitive position.
Interpreting Financial Statement Analysis
Interpreting financial statement analysis involves drawing conclusions and making informed judgments based on the findings. It includes:
- Assessing Financial Performance: Equity researchers assess the company’s performance by analyzing key financial ratios, growth rates, and profit margins. They evaluate revenue trends, profitability drivers, and cost management strategies to gauge the company’s ability to generate sustainable returns.
- Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses: By analyzing financial statements, researchers identify the company’s strengths, such as strong liquidity, robust profitability, or efficient working capital management. They also uncover weaknesses, such as excessive debt levels, declining profitability, or inadequate cash flow generation.
Analyzing financial statements is crucial in equity research as it provides insights into a company’s financial health, performance, and potential risks and returns. Equity researchers can evaluate a company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency, and cash flow generation by examining the income/profit and loss statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. This analysis helps make informed investment decisions and assess the company’s financial strength.
Step 4: Conducting Industry and Competitor Analysis
Conducting industry and competitor analysis is a crucial step in the equity research process. It involves evaluating the broader industry landscape and analyzing competitors to gain insights into a company’s market dynamics, competitive positioning, and growth prospects. This analysis helps equity researchers understand the company’s relative strengths and weaknesses within its industry, identify potential risks and opportunities, and make informed investment decisions.
The Significance of Industry and Competitor Analysis in Equity Research
Industry and competitor analysis plays a vital role in equity research for the following reasons:
- Understanding Industry Dynamics: Analyzing the industry in which a company operates provides insights into its growth potential, market size, and key trends. It helps equity researchers understand the industry’s competitive dynamics, regulatory environment, and macroeconomic factors influencing its performance. This understanding allows researchers to assess the company’s position within the industry and its ability to capitalize on market opportunities.
- Evaluating Competitors: Examining competitors helps researchers benchmark the company’s performance, identify its competitive advantages or disadvantages, and understand the strategies employed by industry peers. By evaluating competitors’ financial performance, product offerings, market share, and competitive positioning, analysts can assess the company’s relative strengths and weaknesses and identify areas for improvement.
Understanding Industry Dynamics
To conduct industry analysis effectively, researchers need to understand key aspects of the industry, including:
- Market Size and Growth Trends: Assessing the industry’s size and growth trends helps researchers gauge the market’s potential and identify expansion opportunities. This analysis includes evaluating historical and projected revenue growth rates, market share data, and industry-specific factors influencing demand.
- Regulatory Environment: Understanding the regulatory environment is crucial for assessing industry risks and compliance requirements. Researchers analyze regulatory frameworks, policies, and potential changes to identify how they may impact the company’s operations, profitability, and growth prospects.
- Competitive Landscape: Analyzing the competitive landscape involves identifying key players in the industry, assessing their market share, and understanding their strategies. This analysis helps researchers evaluate the intensity of competition, identify market leaders, and set the company’s competitive positioning.
Evaluating Competitors
When evaluating competitors, researchers focus on various aspects, including:
- Financial Performance: Analyzing competitors’ financial statements helps researchers compare their revenue growth, profitability, and financial stability with the company being researched. This assessment provides insights into the company’s relative financial strength and performance within the industry.
- Competitive Advantages: Researchers assess competitors’ competitive advantages, such as unique capabilities, market positioning, brand recognition, or cost advantages. Understanding these advantages helps identify potential threats or areas where the company being researched can gain a competitive edge.
- Product and Service Offerings: Evaluating competitors’ product and service offerings helps researchers identify areas of differentiation or potential gaps in the market. This analysis provides insights into consumer preferences, technological advancements, and potential opportunities for the company being researched.
Gathering Industry and Competitor Data
To gather industry and competitor data, researchers rely on various sources, including:
- Industry Reports and Publications: Industry-specific reports, research publications, and trade associations provide valuable insights into market trends, growth forecasts, and industry-specific factors. These sources offer comprehensive data on industry dynamics, competitive forces, and emerging trends.
- Competitor Filings and Disclosures: Reviewing competitors’ filings, such as annual reports, quarterly filings, and investor presentations, helps researchers gather financial and strategic information. These disclosures offer insights into competitors’ business strategies, growth plans, and risk factors.
- Market Research and Analysis: Researchers leverage market research reports, customer surveys, and consumer trends analysis to gather data on market size, consumer preferences, and buying behaviour. This data helps assess market demand and potential opportunities for the company being researched.
Analyzing Industry and Competitor Data
To analyze industry and competitor data effectively, researchers employ various analytical techniques, including:
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) investigation helps researchers identify the company’s core strengths and weaknesses, as well as external prospects and threats in the industry. This analysis helps assess the company’s competitive positioning and potential risks and opportunities.
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis: Porter’s Five Forces analysis evaluates the competitive forces within an industry, including the risk of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry. This analysis helps researchers understand the industry’s competitive dynamics and the company’s ability to navigate these forces.
Conducting industry and competitor analysis is a vital step in equity research. It provides valuable insights into the industry dynamics, competitive landscape, and growth prospects of the company being researched. Analysts can assess the company’s competitive positioning and make informed investment decisions by understanding the industry’s size, trends, and regulatory environment and evaluating competitors’ financial performance and strategies.
Step 5: Valuation Techniques
Valuation techniques play a critical role in equity research, enabling analysts to determine the intrinsic value of a company’s stock. Analysts can use various valuation methodologies to assess whether a company’s stock is overvalued, undervalued, or fairly priced. This step is crucial for making informed investment decisions based on evaluating a company’s future cash flows, growth prospects, and risk factors.
The Significance of Valuation Techniques in Equity Research
Valuation techniques are of great significance in equity research for the following reasons:
- Determining Intrinsic Value: Valuation techniques help analysts estimate the intrinsic value of a company’s stock by assessing its future cash flows, growth potential, and risk factors. This estimation lets investors decide about buying, selling, or holding a particular stock.
- Comparative Analysis: Valuation techniques enable analysts to compare a company’s value to its peers and industry standards. This comparison helps identify a sector’s strengths, weaknesses, and investment opportunities.
Purpose of Valuation
The primary purpose of a valuation is to estimate the reasonable value of a company’s stock based on its underlying fundamentals, market conditions, and prospects. Valuation serves the following purposes:
- Investment Decision Making: Valuation techniques help investors determine whether a stock is a worthwhile investment opportunity based on its estimated intrinsic value. It assists in identifying potential undervalued stocks that may provide higher returns in the long term.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Valuation plays a crucial role in assessing the value of a target company during mergers and acquisitions. It helps determine the purchase price and negotiate a fair deal for both parties.
- Fundamental Analysis: Valuation is an essential component of fundamental analysis. It assists in evaluating a company’s financial health, growth prospects, and potential risks.
Common Valuation Techniques
Several valuation techniques are commonly used in equity research:
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis: DCF analysis estimates the present value of a company’s future cash flows by discounting them back to their current value. This technique considers the time value of money and helps determine the intrinsic value of a company’s stock.
- Comparable Company Analysis: Comparable company analysis involves comparing a company’s financial ratios, such as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, price-to-sales (P/S) ratio, or price-to-book (P/B) ratio, with similar companies in the industry. This analysis helps assess whether the company’s stock is overvalued or underrated compared to its peers.
- Precedent Transactions Analysis: Precedent transactions analysis involves analyzing the valuation multiples of previous acquisitions or mergers within the industry. It helps determine the appropriate valuation multiples for a company based on historical transactions.
Factors Influencing Valuation
Several factors influence the valuation of a company’s stock:
- Company-Specific Factors: Company-specific factors, such as financial performance, growth prospects, competitive advantage, management quality, and risk profile, significantly impact the valuation. Positive aspects may result in a higher valuation, while negative aspects may lead to a lower valuation.
- Industry and Market Factors: Industry and market factors, including market demand, industry growth prospects, competitive landscape, and regulatory environment, affect a company’s valuation. A company operating in a high-growth industry with favourable market conditions may receive a higher valuation.
- Macroeconomic Factors: Macroeconomic aspects, such as interest rates, inflation rates, GDP growth, and overall market conditions, influence the valuation of stocks. Economic factors can impact a company’s cash flows, discount rates, and market sentiment, leading to changes in its valuation.
Limitations of Valuation Techniques
It is important to acknowledge the limitations of valuation techniques:
- Future Uncertainty: Valuation techniques rely on making assumptions about a company’s future performance, which introduces uncertainty. Changes in market conditions, industry dynamics, or company-specific factors can impact the accuracy of the valuation.
- Subjectivity: Valuation techniques require subjective judgments in selecting appropriate assumptions, discount rates, and comparable companies. Different analysts may have varying opinions, leading to other valuations.
- Market Efficiency: Valuation techniques assume markets are efficient and prices reflect all available information. However, market inefficiencies and behavioural biases can result in mispricing, leading to disparities between estimated valuations and actual market prices.
Valuation techniques are an essential step in equity research, enabling analysts to estimate the intrinsic value of a company’s stock. Analysts can assess the company’s value relative to its fundamentals and industry peers through discounted cash flow analysis, comparable company analysis, and precedent transactions analysis. However, it is important to consider the limitations and factors influencing valuation to make informed investment decisions.
Step 6: Formulating Investment Recommendations
Formulating investment recommendations is a crucial step in equity research, as it guides investors regarding buying, selling, or holding a particular stock. This step involves analyzing research findings, considering various factors, and developing a balanced view of a company’s investment potential. Investment recommendations help investors make informed decisions and manage their portfolios effectively.
The Importance of Formulating Investment Recommendations
Formulating investment recommendations is important for several reasons:
- Guiding Investor Decisions: Investment recommendations provide investors with actionable insights and guidance on allocating their investment capital. They help investors make informed decisions by analyzing a company’s financial performance, industry dynamics, competitive positioning, and risk factors.
- Managing Risk: Investment recommendations help investors manage risk by identifying pitfalls and highlighting companies with strong growth potential. They provide a framework for diversification and risk management within an investment portfolio.
- Building Trust: Investment recommendations are based on thorough analysis and research, which helps build trust between equity researchers and investors. Researchers establish credibility and foster long-term client relationships by providing well-reasoned and transparent recommendations.
Analyzing Research Findings
Before formulating investment recommendations, equity researchers thoroughly analyze their research findings. They review financial statements, industry reports, competitive analyses, valuation assessments, and other relevant data to understand the company and its investment potential comprehensively. This analysis forms the basis for investment recommendations.
Factors Considered in Formulating Investment Recommendations
Several factors are considered when formulating investment recommendations:
- Financial Performance and Health: Researchers assess a company’s financial performance, including revenue growth, profitability, cash flow generation, and debt levels. A strong financial position and consistent performance are positive indicators for an investment recommendation.
- Industry and Market Trends: Researchers evaluate industry trends, market dynamics, and macroeconomic factors that may impact the company’s prospects. Understanding the industry’s growth potential and market conditions helps researchers gauge the company’s future opportunities and challenges.
- Competitive Positioning: Assessing a company’s competitive positioning is crucial for formulating investment recommendations. Researchers analyze the company’s market share, competitive advantages, product differentiation, and ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Risk Assessment: Researchers identify and assess potential risks of investing in a particular company. They evaluate operational risks, market risks, regulatory risks, and other factors that may impact the company’s performance and investment potential.
- Valuation Analysis: Valuation analysis is an integral part of formulating investment recommendations. Researchers compare the company’s valuation metrics, such as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, price-to-sales (P/S) ratio, or discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, with industry peers and market benchmarks to determine whether the stock is undervalued, overvalued, or fairly priced.
Developing a Balanced View
Equity researchers aim to develop a balanced view when formulating investment recommendations. They consider a company’s positive and negative aspects, weighing the risks and rewards associated with investing in it. By taking a comprehensive and objective approach, researchers provide a fair assessment of the investment potential and help investors make well-informed decisions.
Communicating Investment Recommendations
Clear and effective communication of investment recommendations is crucial. Researchers provide detailed reports or summaries, clearly explaining the rationale behind their recommendations. They use concise language, avoid jargon, and present information in an easily understandable format for investors. Communication may include target prices, expected returns, time horizons, and potential risks.
Formulating investment recommendations is a critical step in equity research. It helps guide investor decisions, manage risk, and build trust between researchers and investors. By thoroughly analyzing research findings, considering various factors, developing a balanced view, and effectively communicating recommendations, equity researchers provide valuable insights that empower investors to make informed investment decisions.
Step 7: Monitoring and Updating Research
Monitoring and updating research is a crucial step in equity research that ensures the accuracy and relevance of investment recommendations over time. As the financial markets and companies continuously evolve, monitoring and updating studies allows equity researchers to stay informed, identify company fundamentals and market dynamics changes, and adjust investment recommendations accordingly. This step is vital for maintaining the quality and effectiveness of equity research.
The Importance of Monitoring and Updating Research
Monitoring and updating research is important for several reasons:
- Accuracy and Relevance: Regular monitoring and updating of research ensure that investment recommendations remain accurate and relevant in light of changing market conditions, industry trends, and company performance. It helps avoid outdated information and enables timely adjustments to recommendations.
- Risk Management: Equity researchers can identify and manage potential investment risks by continuously monitoring a company’s performance and market dynamics. This proactive approach allows for risk mitigation and timely decision-making to protect investor portfolios.
- Opportunity Identification: Monitoring and updating research enable researchers to identify new investment opportunities as they arise. Researchers can provide timely recommendations that capture potential growth opportunities by staying informed about market developments, emerging trends, and innovative companies.
Continuous Monitoring of Company Performance
Equity researchers continuously monitor a company’s performance to stay abreast of its financial health, operational efficiency, and strategic initiatives. It involves:
- Financial Analysis: Regular analysis of financial statements, including income/profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, helps assess a company’s profitability, liquidity, and solvency. Monitoring key financial ratios, such as return on equity (ROE), earnings per share (EPS), and debt-to-equity ratio, provides insights into the company’s business performance.
- News and Event Tracking: Keeping track of news, press releases, and corporate events related to the company helps identify significant developments that may impact its performance and valuation. It includes mergers and acquisitions, product launches, regulatory changes, and management updates.
Chasing Industry and Market Trends
Equity researchers also monitor industry and market trends to understand the broader context in which a company operates. It involves:
- Industry Research: Tracking industry reports, market analyses, and industry-specific news helps researchers identify shifts in market demand, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and competitive dynamics. This knowledge allows for a comprehensive assessment of a company’s competitive positioning and growth potential.
- Macroeconomic Analysis: Monitoring macroeconomic indicators, such as interest rates, inflation rates, GDP growth, and geopolitical developments, helps researchers evaluate the overall market environment and its potential impact on investment decisions. Understanding macroeconomic trends provides insights into the broader investment landscape.
Reviewing and Revising Investment Recommendations
Based on the insights gained from continuous monitoring, equity researchers review and revise their investment recommendations as necessary. It includes:
- Updating Financial Models: Incorporating new financial data and adjusting financial models based on changing assumptions ensures that the company’s valuation remains current. It allows for a more accurate assessment of the company’s intrinsic value.
- Reassessing Risk Profiles: As market conditions change, equity researchers reassess the risk profiles associated with specific investments. It may involve adjusting risk assessments, considering new risk factors, or recommending risk management strategies.
Staying Informed and Up-to-Date
To effectively monitor and update research, equity researchers stay informed and up-to-date through:
- News and Information Sources: Regularly accessing reputable news sources, financial publications, industry journals, and research reports helps researchers stay informed about market developments, industry trends, and company-specific news.
- Professional Networks: Engaging with industry experts, attending conferences, and participating in professional networks provide opportunities to exchange ideas, gain insights, and stay updated on the latest industry knowledge.
Monitoring and updating research is a fundamental step in equity research that ensures investment recommendations’ accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. By continuously monitoring company performance, tracking industry and market trends, reviewing and revising recommendations, and staying informed, equity researchers can provide investors with valuable insights and guidance to make informed investment decisions.
Conclusion
Equity research is vital in investment decision-making by providing valuable insights and analysis. By following a step-by-step process that includes defining the research objective, gathering relevant data, analyzing financial statements, conducting industry and competitor analysis, using valuation techniques, formulating investment recommendations, and monitoring the research, analysts can generate comprehensive reports that assist investors in making informed choices.
Note: This blog provides an overview of the step-by-step process of equity research. It is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Investors are advised to consult a qualified financial professional before making investment decisions.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What skills are required to perform equity research effectively?
Effective equity research requires strong analytical skills, financial acumen, and industry knowledge. It also demands proficiency in financial modelling, data analysis, and valuation techniques. Additionally, effective communication and the ability to articulate complex information clearly and concisely are essential.
Is equity research limited to large financial institutions?
No, equity research is conducted by various market participants, including sell-side analysts from financial institutions, buy-side analysts from asset management firms, and independent research providers. It caters to the needs of individual investors, institutional investors, and financial professionals.
How can equity research benefit individual investors?
Equity research provides individual investors valuable insights into specific companies, industries, and investment opportunities. It helps them make well-versed decisions based on thorough analysis and research, enabling them to maximize their investment returns and manage their portfolios effectively.
Can equity research help in identifying investment risks?
Yes, equity research aids in identifying and assessing investment risks. Analysts can identify potential risks associated with specific investments by conducting industry and competitor analysis, analyzing financial statements, and evaluating market dynamics. This information helps investors make more informed decisions and manage their risk exposure.
How can one access equity research reports?
Equity research reports are typically available through financial institutions, brokerage firms, and independent research providers. Investors can access these reports through online platforms, financial news websites, or by subscribing to research services offered by these institutions.
Disclaimer:
This blog is solely for educational purposes. The securities/investments quoted here are not recommendatory. This is not an investment advisory. The blog is for information purposes only. Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks. Read all the related documents carefully before investing.
Past performance is not indicative of future returns. Please consider your specific investment requirements, risk tolerance, goal, time frame, risk and reward balance, and the cost associated with the investment before choosing a fund or designing a portfolio that suits your needs. The performance and returns of any investment portfolio can neither be predicted nor guaranteed.
The information provided in this article is solely the author/advertisers’ opinion and not investment advice – it is provided for educational purposes only. Using this, you agree that the information does not constitute any investment or financial instructions by Ace Equity Research and the team. Anyone wishing to invest should seek their own independent financial or professional advice. Do conduct your research along with registered financial advisors before making any investment decisions. Ace Equity Research and the team are not accountable for the investment views provided in the article.


